When it comes to cybersecurity, one-and-done fixes just don't cut it. Real security is a continuous cycle of vigilance. The vulnerability management process is the engine that drives this cycle, giving businesses a systematic way to find, evaluate, fix, and confirm security weaknesses across their entire digital footprint. Think of it as a foundational pillar of any modern cyber defense strategy.
Why Vulnerability Management Is a Business Imperative

Picture vulnerability management like the routine maintenance of a historic building. You wouldn't wait for a wall to crumble before checking the foundation for cracks. You'd proactively inspect the structure, reinforce weak spots, and address potential issues long before they become catastrophic failures. This process does the same for your digital assets, helping you find and patch security holes before attackers can break in.
This guide isn't just a technical checklist. It's a look at vulnerability management as a core business function—a strategic approach that builds resilience, protects your bottom line, and ensures you can thrive in an age of constant cyber threats.
Moving Beyond Reactive Fixes
Too many organizations get stuck in a reactive "firefighting" mode, only scrambling to fix security problems after a breach has already happened. A formal vulnerability management process flips that script, moving you from a reactive posture to a proactive one by creating a structured system for constant improvement.
The main goals here are to:
- Reduce the Attack Surface: Methodically find and close the security gaps that attackers use as entry points.
- Prioritize Real Threats: Focus your team's limited time and resources on fixing the vulnerabilities that pose the biggest danger first.
- Maintain Compliance: Satisfy the strict requirements of regulations like HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR, all of which demand robust security programs.
- Build Stakeholder Confidence: Show customers, partners, and investors that you are serious about protecting their data and your company's intellectual property.
This forward-thinking stance is critical for keeping the lights on. You can dig deeper into this connection by exploring the importance of cybersecurity for growing businesses.
Vulnerability management is the cornerstone of any robust information security program. Classifying risks allows organizations to identify, prioritize, and address the highest-risk items more quickly, reducing the likelihood that vulnerabilities posing the greatest risk will be exploited.
A Growing Market Driven by Necessity
The sheer volume and sophistication of modern cyberattacks have made this process non-negotiable for businesses of all sizes. This isn't just an observation; it's a reality reflected in the market's explosive growth.
As of 2025, the global vulnerability management market is already valued at over $16 billion. Projections show it could swell to as much as $30.36 billion by 2033, a surge driven by the relentless need for stronger defensive tools and strategies. You can discover more about these market forecasts and their drivers.
Discovering Your Entire Digital Footprint
Let's start with a fundamental truth in cybersecurity: you cannot protect what you do not know exists. This simple idea is the entire point of the first, and arguably most critical, phase of any vulnerability management program: discovery.
Think of it as creating a detailed, living map of every single digital asset connected to your business. This is the foundation upon which everything else is built.
We're not just talking about the servers in your data center or the laptops on everyone's desks. Today's IT environment is a sprawling, chaotic mix of cloud servers, employee mobile phones, IoT sensors, operational technology (OT) on the factory floor, and the ever-present 'shadow IT'—apps and services your teams use without getting a thumbs-up from IT. Without a complete inventory, you’re essentially trying to secure your house while leaving the back door wide open.
From Unknowns to a Complete Inventory
The main goal here is to turn all those unknown devices and applications into known, managed assets. This isn't a one-and-done task; it's a continuous process that uses specialized tools to sweep your network and pinpoint every connected device.
You'll typically rely on a few key methods:
- Network Scanners: These are the bloodhounds of asset discovery. Tools like Nessus or Qualys systematically probe your network to see which devices are online, what ports are open, and what services they're running.
- Asset Management Databases: A good Configuration Management Database (CMDB) acts as your central source of truth. When you feed data from your scanners into the CMDB, you get a unified, reliable view of all your IT assets and how they connect.
- Endpoint Agents: For devices that come and go from the corporate network, like remote laptops, software agents are key. These small programs installed on the device regularly report back detailed information, ensuring nothing falls through the cracks.
This infographic gives you a great visual of how these different discovery methods come together to map out a modern, interconnected network.
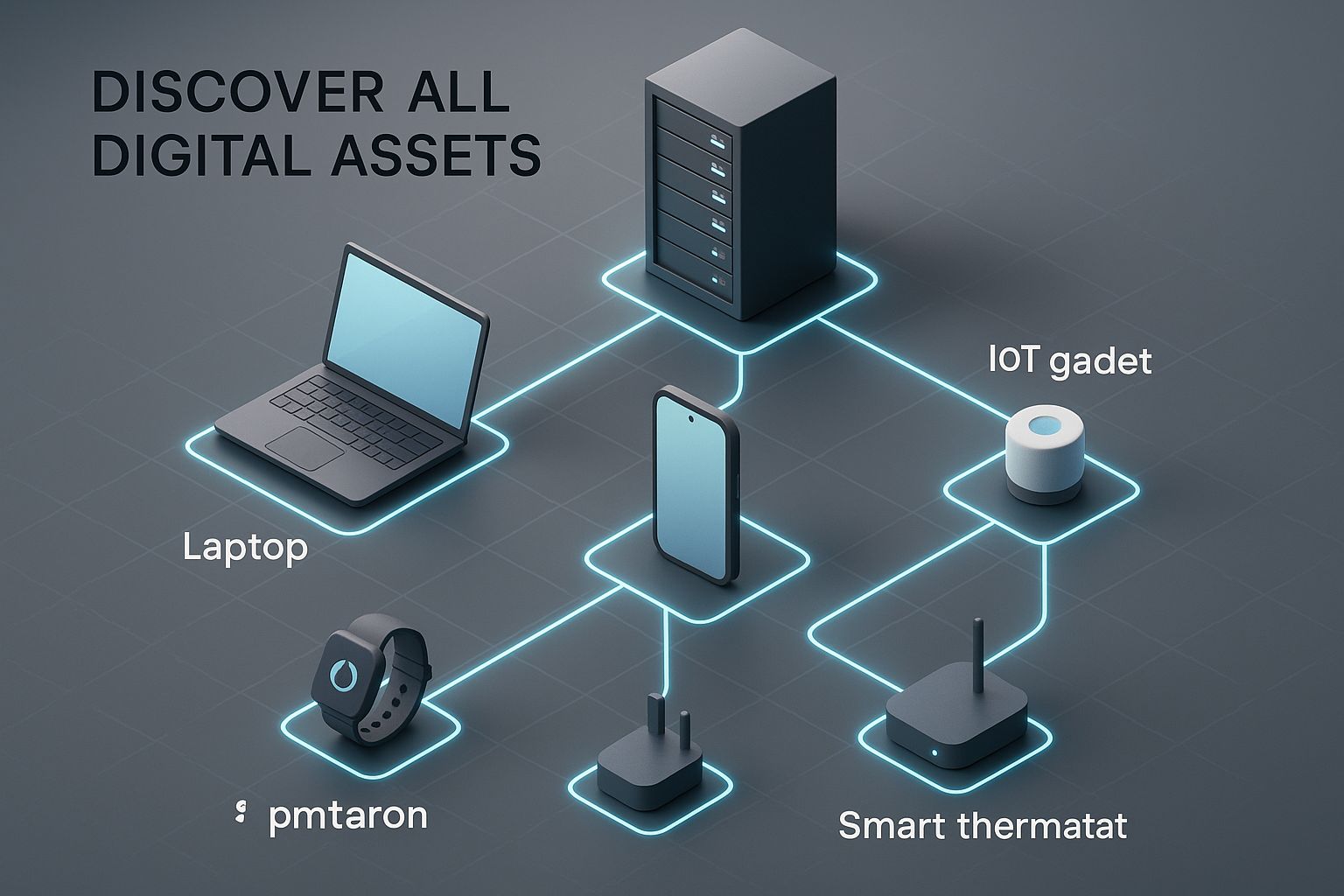
As you can see, it's a complex ecosystem, not just a simple list. That’s why you need a multi-pronged approach to get the full picture.
Why Comprehensive Discovery Is Non-Negotiable
A spotty asset inventory is a classic security failure. That unmanaged server tucked away in a closet, a forgotten cloud instance, or an unsanctioned file-sharing app can easily become the front door for an attacker.
Getting discovery right pays dividends across the entire security program.
An accurate asset inventory is the bedrock of a risk-based security strategy. It moves you from just knowing what you have to understanding which assets are most critical to keeping the business running. This ensures you focus your time and money where it counts the most.
When you can see every piece of hardware and software, you can finally apply security policies consistently, run meaningful risk assessments, and make sure no corner of your digital world is left exposed. This initial step transforms a chaotic, unknown environment into one that is manageable and, most importantly, defensible.
Assessing and Prioritizing Real-World Risks
Once you’ve mapped out your digital assets, the real work begins. You're not just looking at a few isolated issues; you're likely staring down a list of thousands of potential vulnerabilities. It's an overwhelming amount of noise. This is where the next critical phase—assessment and prioritization—comes into play.
The goal here is to cut through the clutter and pinpoint the handful of threats that actually endanger your business. It's about turning a giant, messy list of problems into a strategic, actionable plan.
Think of it like being an emergency room doctor. When a flood of patients arrives, you don't just treat them in the order they came through the door. You perform triage—quickly assessing who needs immediate, life-saving intervention. This risk-based approach ensures your most critical resources go where they’ll make the biggest difference.
Moving Beyond Simple Scores
For years, security teams leaned heavily on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). It assigns a numerical score to each vulnerability, with 10.0 being the most severe. While it’s a useful starting point, relying only on CVSS scores is like a doctor diagnosing a patient based solely on their temperature. It's an important piece of data, but it hardly tells the whole story.
A vulnerability with a high CVSS score sitting on an isolated, non-critical test server poses far less real-world risk than a medium-score flaw on your primary, customer-facing database. When you fixate on CVSS scores alone, you create "alert fatigue." Your team ends up wasting precious time chasing low-impact issues while the truly dangerous threats get buried in the backlog.
The foundation of smart prioritization is a thorough cybersecurity risk assessment, which provides a clear roadmap for identifying and ranking threats based on what matters to your organization.
Layering Context for True Prioritization
A mature vulnerability management program enriches raw vulnerability data with critical business context. This is what separates a reactive, firefighting team from a proactive, strategic one. Instead of asking, "How high is the score?" the better question is, "How much does this vulnerability actually matter to us right now?"
Here are the key layers of context you need to add:
- Asset Criticality: How important is the affected system? A vulnerability on your public-facing e-commerce server is infinitely more urgent than the same flaw on an internal development machine.
- Threat Intelligence: Are hackers actively exploiting this vulnerability in the wild? Real-time threat intelligence tells you which vulnerabilities have become weapons for active attack campaigns, bumping them to the top of your list.
- Exploitability: How easy is it for an attacker to leverage this weakness? Some vulnerabilities require deep system access and complex maneuvers, making them less of an immediate threat than those that can be exploited with a simple, widely available script.
- Business Impact: If this asset were compromised, what would the damage be? Think in terms of financial loss, reputational harm, operational downtime, and regulatory penalties.
This constant flood of new vulnerabilities makes a structured prioritization framework non-negotiable. The numbers are staggering—over 30,990 vulnerabilities were reported globally in 2025 alone. Within that, more than 21,500 were assigned CVE identifiers, and 38% of those were rated high or critical. The threat landscape is not just growing; it's exploding.
A risk-based approach transforms vulnerability management from a technical box-ticking exercise into a strategic business function. It ensures that every hour your security team spends is dedicated to reducing the most significant and immediate risks to the organization.
Vulnerability Prioritization Framework Comparison
To really see the difference, it helps to compare the old way of thinking with a modern, risk-based approach. The table below shows just how much the outcome changes when you start adding context to your decision-making.
| Factor | CVSS-Based Prioritization | Risk-Based Prioritization |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Driver | Relies almost exclusively on the vulnerability's technical severity score (e.g., CVSS 9.8). | Considers the CVSS score as just one data point among many, including asset value and threat intelligence. |
| Typical Outcome | A long, unmanageable list of "critical" items, leading to team burnout and unresolved high-risk issues. | A focused, manageable list of the top threats that pose a clear and present danger to business operations. |
| Resource Focus | Wastes time and effort on high-scoring vulnerabilities that exist on low-impact, non-critical systems. | Directs resources to fix vulnerabilities on the most critical assets, maximizing risk reduction. |
| Decision Making | Often rigid and automated, treating every high score as a top priority without any human judgment. | Blends automated data with human analysis to make informed decisions based on the unique context of the business. |
By adopting this smarter, context-aware assessment, your team stops chasing ghosts and starts neutralizing genuine threats. This pragmatic focus is the only way to effectively manage risk when you're facing an ever-expanding attack surface.
Taking Action to Remediate Vulnerabilities

You’ve identified your assets and lined up your risks from most to least critical. Now it’s time to roll up your sleeves and shift from planning to doing. This is the remediation phase, where your team moves in to neutralize the threats you’ve uncovered.
This isn’t just about blindly deploying a software patch. It’s a carefully coordinated operational effort to fix weaknesses without accidentally causing new problems.
Think of it like a surgical procedure. Your IT and security teams are the surgeons who’ve reviewed the scans (vulnerability reports) and pinpointed the problem. Now, they have to perform the operation—apply the fix—with precision and skill, all while communicating clearly to ensure the patient (your system) recovers perfectly with no side effects.
Choosing the Right Treatment Strategy
Not every vulnerability gets the same fix. The right approach depends on the risk level, whether a patch is even available, and how much disruption fixing it might cause. Your team will generally choose one of three primary strategies.
Here’s how they break down:
- Remediation: This is the best-case scenario and the most common goal. It means applying a direct fix, like a software patch or a configuration change, that completely closes the security hole for good.
- Mitigation: When a full fix isn't available yet—think of a zero-day attack—this is your go-to move. Mitigation involves putting up temporary defenses, like tightening firewall rules or restricting access, to make the vulnerability much harder to exploit and reduce its potential impact. It buys you valuable time.
- Acceptance: Let’s be realistic: sometimes the cure is worse than the disease. For a low-risk flaw on a non-critical system, the cost and effort to fix it might be far greater than the potential damage. In these specific cases, leadership can make a formal, documented decision to accept the risk.
Orchestrating the Response
Fixing vulnerabilities is a team sport. It requires a collaborative effort, not a siloed one.
Imagine a critical zero-day flaw is found in your company’s main web application. This is no time for panic. A well-oiled vulnerability management process brings the right people together to execute a clear plan.
The security team validates the threat and briefs the IT operations and development teams. If a vendor patch isn't out yet, the dev team might get to work on a custom one. At the same time, the IT team could deploy mitigation measures, using a web application firewall to block traffic patterns that target the flaw. This kind of coordinated response neutralizes the immediate danger while a permanent solution is put in place.
A successful remediation phase hinges on clear communication and defined responsibilities. When everyone knows their role and the clock is ticking, teams can execute fixes efficiently, minimizing both security risk and operational downtime. This level of coordination is a hallmark of a mature security program.
Establishing Clear Rules of Engagement
To keep things from descending into chaos, mature programs run on predefined rules, often formalized in Service Level Agreements (SLAs). These agreements set crystal-clear expectations for how quickly vulnerabilities must be addressed based on their severity.
A typical SLA framework might look something like this:
| Severity Level | Remediation SLA | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Critical | Within 24-72 hours | A remote code execution flaw on a public-facing, internet-connected payment server. |
| High | Within 15-30 days | A privilege escalation bug on an internal database server containing sensitive data. |
| Medium | Within 60-90 days | A cross-site scripting (XSS) flaw on a low-traffic internal administrative portal. |
| Low | Within 180 days or during next update | Outdated software on an isolated R&D machine with no connection to the main network. |
These SLAs turn remediation from a frantic guessing game into a predictable, measurable process. They create accountability and help teams prioritize their workload without getting overwhelmed. For organizations that need a hand defining and managing these processes, exploring professional managed cybersecurity services can provide the expert structure needed to build a resilient defense.
Verifying Fixes and Reporting on Progress
So, you’ve applied the patch. Job done, right? Not so fast.
Applying a fix is just one part of the puzzle. The final, and frankly, most critical phase is verifying that the fix actually worked and then reporting on that progress. This is where you close the loop, proving that your efforts paid off and showing the rest of the business what you’ve accomplished.
Think of it like a quality check on a manufacturing line. After a car is assembled, it goes through a final inspection to make sure every part is secure and it runs correctly before it leaves the factory. In the same way, this phase confirms that a vulnerability is truly gone and that the fix didn't accidentally break something else.
This isn’t just a technical box to tick; it's about accountability. It demonstrates the value of your security program and gives you the data needed to keep improving.
Confirming Successful Remediation
The first thing you need to do is confirm the fix stuck. It's a common and dangerous mistake to just trust that a patch was deployed successfully without double-checking. Patches can fail to install, configurations can be misapplied—all sorts of things can go wrong, leaving you exposed even after all that hard work.
Security teams usually rely on a few trusted methods to validate fixes:
- Follow-Up Scans: The most straightforward way is to simply re-scan the asset with your vulnerability scanner. If the vulnerability is gone from the report, you can be reasonably sure the fix was successful.
- Penetration Testing: For your most critical vulnerabilities, a targeted pen test is the gold standard. A tester will actively try to exploit the patched system, giving you the ultimate confirmation that the weakness has been eliminated.
- Configuration Audits: Sometimes a fix isn't a patch but a settings change. An audit confirms that the new, secure configuration is in place and has been applied correctly across the board.
This validation step is non-negotiable. It's what prevents "ghost" vulnerabilities—those pesky issues you think are fixed but are still waiting to be exploited.
Crafting Reports for Different Audiences
Once you've verified the fix, it’s time to talk about it. But a one-size-fits-all report is a recipe for disaster. What a network engineer needs to know is worlds apart from what a CEO or an auditor cares about. Good reporting is all about tailoring the message to the person reading it.
Reporting is how you translate raw security data into a business story. It shows how you're reducing risk, proves you're compliant, and justifies the money and time spent on your security program. When done right, it makes the value of your work visible to everyone.
You'll likely need a few different types of reports:
- For Technical Teams: These folks need the nitty-gritty. Think detailed dashboards showing patching status, how long remediation is taking, and the raw scan results. This helps IT operations track their work and spot any snags in the process.
- For Executive Leadership: The C-suite needs the big picture, connecting security work to business goals. Reports for leaders should focus on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) like overall risk score reduction, Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR), and trends in critical vulnerabilities over time.
- For Compliance and Auditors: This is all about evidence. These reports need to clearly document that your organization is meeting its regulatory requirements. With frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS all mandating strong vulnerability management to protect data, solid reporting is essential to avoid hefty fines. If you want to dive deeper into these requirements, you can discover more about choosing a vulnerability management solution.
Building a Mature and Proactive Program
Getting ahead of vulnerabilities means graduating from a reactive, fire-fighting mode to a truly proactive security stance. This isn't just about following a checklist. It's about building a mature program where the vulnerability management process is a strategic, data-driven engine woven right into the fabric of your business.
This evolution is less about the tools you buy and more about your people, strategy, and culture. A mature program demolishes the silos between IT, security, and development teams, creating a culture of shared ownership. When everyone understands their part and is held accountable, real progress happens.
Shifting to a Proactive Culture
A proactive culture is built on a foundation of clearly defined roles and responsibilities. When a critical vulnerability pops up, there should be zero confusion about who owns the patch, who tests the fix, and who keeps leadership in the loop.
This shift is often called moving security "left"—embedding it earlier in the development and operations lifecycle. To get there, you have to integrate security into every stage, a concept often called DevSecOps. Digging into DevOps Security best practices is a great way to see how this integration works in the real world.
A mature vulnerability management program is not just a security team’s responsibility; it’s an organizational commitment. It transforms security from a gatekeeper into an enabler of secure, resilient business operations.
Measuring What Matters Most
If you can't measure it, you can't improve it. A mature program is defined by its ability to track meaningful metrics that highlight effectiveness, expose bottlenecks, and prove its value. This goes way beyond just counting how many vulnerabilities you've patched.
Instead, you need to focus on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that actually tell the story of risk reduction:
- Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR): This is the gold standard. It’s the average time it takes your team to fix a vulnerability from the moment it’s discovered. If this number is going down, you're on the right track.
- Scan Coverage: What percentage of your digital assets are you actually scanning? You can't protect what you can't see, so aiming for 100% coverage is non-negotiable for eliminating blind spots.
- Vulnerability Re-open Rate: How often do you find a vulnerability that you thought was fixed? A high re-open rate is a red flag, often pointing to botched patches or rushed, sloppy work.
Tracking these KPIs creates a powerful feedback loop. It gives you the hard data you need to justify budgets, hold teams accountable, and continuously dial in your defenses. Many businesses find that an expert partner provides the framework needed to implement and monitor these metrics. It’s a key reason why so many San Antonio businesses trust DefendIT Services for cybersecurity and IT solutions, gaining a dedicated partner to help build this level of maturity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Even with a solid grasp of the four phases, turning theory into practice is where the real work begins. Questions always come up when you start building a vulnerability management process from the ground up, from choosing the right tools to getting teams to work together smoothly.
Let’s tackle some of the most common questions we hear from organizations trying to get this right.
How Often Should We Scan for Vulnerabilities?
There's no single magic number here—the right scanning schedule really depends on what you're trying to protect. A generic, one-size-fits-all approach just doesn’t cut it. The key is to segment your assets and match your scanning frequency to the risk.
-
External, Public-Facing Systems: Think of these as your digital storefront. Anything directly facing the internet—like your web servers or VPNs—is a prime target and needs constant attention. You should be scanning these at least weekly, if not daily.
-
Internal Production Systems: Your critical internal servers, databases, and applications that handle sensitive data are the crown jewels. A weekly or bi-weekly scan is a good starting point to keep them secure.
-
Lower-Risk Environments: Your development and testing environments are less critical, so you can usually get away with scanning them monthly.
Remember, these scheduled scans are just your baseline. You should always run an on-demand scan after any major event, like rolling out a new application or spinning up a new server.
The real goal isn't just finding vulnerabilities; it's finding them before an attacker does. Your scanning schedule for critical systems needs to be faster than an attacker's timeline for discovering and exploiting a new weakness.
What’s the Difference Between a Vulnerability Assessment and a Penetration Test?
This is a big one, and people mix them up all the time. They are not the same thing, but they work together beautifully.
Think of a vulnerability assessment (or scan) as casting a wide net. It's an automated process that sweeps across your systems to find a broad range of potential security weaknesses. It’s like a comprehensive health checkup that flags everything that looks out of place, answering the question, "What weaknesses might we have?"
A penetration test (pen test), on the other hand, is a focused, hands-on attack simulation. An ethical hacker takes the list of potential weaknesses and tries to actively exploit them to see if they can break in and cause real damage. It answers a much more pointed question: "Can this weakness actually be used against us?"
A mature vulnerability management process is the bedrock of modern cybersecurity, but it demands constant effort and deep expertise. Defend IT Services offers the strategic guidance and hands-on support to build and run a program that shrinks your attack surface and safeguards your most important assets. Get a customized security roadmap by visiting our website at https://defenditservices.abyusuf.com.



